Prof. Ziyang Lu’ group published an article on Applied Catalysis B: Environmental (IF=24.319) with the title of "Rapid dissociation of high concentration excitons between [Bi2O2]2+ slabs with multifunctional N-Bi-O sites for selective photoconversion into CO" which was also invited to push reports on the "Environmental Advances" WeChat official account.

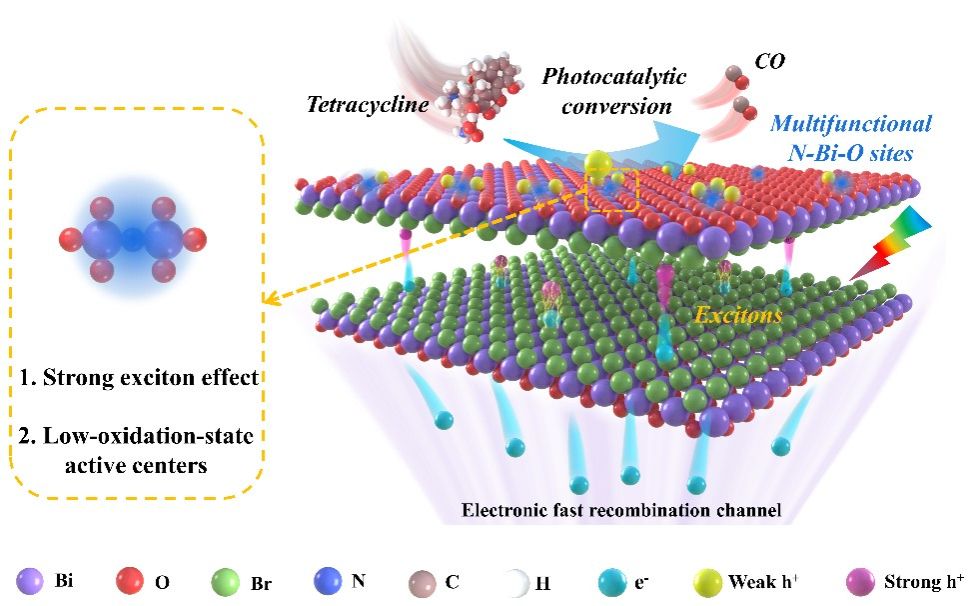
Regulation of exciton generation and dissociation, directed transfer to active center and oxidation capacity are the key steps in photoconversion. Here, we report that the multifunctional N-Bi-O sites are prepared in BiOBr nanosheets without the introduction of oxygen vacancy to reduce localized overreaction centers, which can not only enhance the Coulomb force between [Bi2O2]2+ slabs, thus increasing the exciton concentration, but also form low-oxidation-state active centers which can serve as the selective reaction sites and hole capture sites. Additionally, electronic fast recombination channels promote rapid dissociation of excitons and synergistic attraction to low-oxidation-state active centers to form weak holes. These holes prefer to rapid photoconversion of TC into CO instead of CO2. The yield of selective photoconversion into CO is 43.53 µmol/g, and the proportion of CO products is 16.21%. This work proposes a strategy for the cooperative construction of multifunctional active centers and multiexciton dissociation structures.
Full text link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926337323005350
“Environmental Advances” WeChat official account push report link:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/-7TSy1iqFjbmMvmkKEn71g


